Intraday trading, a strategy based on short-term movements within the trading day, requires a deep understanding of chart patterns to predict future price movements effectively. This article delves into the intricacies of intraday trading chart patterns, offering insights into how traders can leverage these patterns for better decision-making in the fast-paced trading environment.
In this article:
Best Intraday Trading Chart Patterns:
Tools and Resources for Chart Pattern Trading
Advanced Strategies in Chart Pattern Trading
What is Intraday Trading?
Intraday trading, often referred to as day trading, is a trading strategy where financial instruments are bought and sold within the same trading day. The objective is to capitalize on small price movements in the market over a short period. Traders involved in intraday trading look to leverage high volumes of trades to secure small profits from each, which can cumulatively lead to significant gains. This form of trading requires a keen understanding of market trends, the ability to make quick decisions, and a thorough risk management strategy to mitigate potential losses.

Unlike long-term investments, where the focus is on potential future value growth over years or even decades, intraday trading is all about the fluctuations that occur within the market hours of a single day. It demands constant monitoring of the market, as traders must enter and exit positions swiftly to capture profit from short-term movements. This trading style is popular among those seeking to avoid the risk of overnight market volatility affecting their positions. However, it also requires a high level of discipline, a good grasp of technical analysis, and an ability to remain calm under pressure to be successful.
What Are Chart Patterns?
Chart patterns are formations within price charts that help predict future price movements based on historical trends. These patterns are foundational to technical analysis and are used extensively in intraday trading to make informed decisions.
Why Are They Important for Intraday Traders?
Intraday traders rely on chart patterns to make quick, informed decisions. The ability to recognize and interpret these patterns allows traders to anticipate market movements and manage risk more effectively.
Types of Chart Patterns
Reversal Patterns
Continuation Patterns
Head and Shoulders
Pennant or Flags
Double Top
Ascending Triangle
Double Bottom
Descending Triangle
Rounding Bottom
Symmetrical Triangle
Cup and Handle
Wedges
1. Head and shoulders
The Head and Shoulders pattern is a highly regarded reversal pattern in the realm of technical analysis, often signaling a shift in market trend from bullish to bearish. Characterized by three peaks, with the middle peak (the head) being the highest and the two outer peaks (shoulders) at lower heights, this pattern emerges in an uptrend, indicating that a reversal to a downtrend is imminent. The "neckline," drawn by connecting the low points after the first and second peaks, serves as a critical point of reference. A decisive break below this neckline confirms the pattern, suggesting that sellers have overtaken buyers and a new bearish trend is beginning.
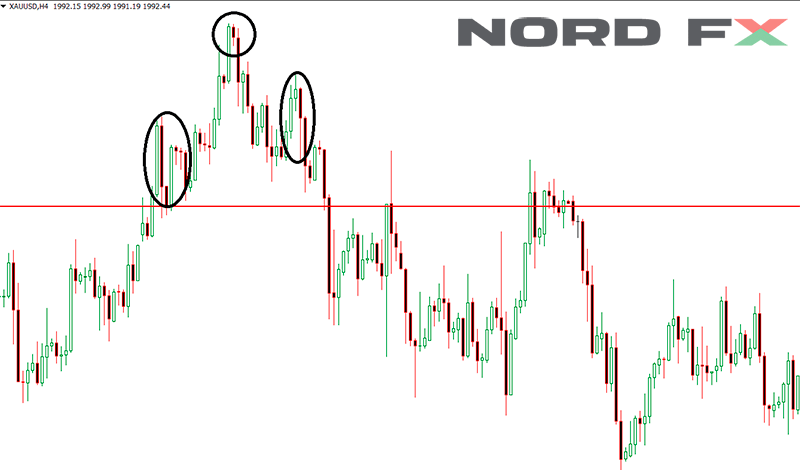
Traders pay close attention to the Head and Shoulders pattern for its reliability and potential predictive power regarding future market movements. Upon identification of this pattern, traders often wait for a break below the neckline before executing sell orders to capitalize on the anticipated downward movement. Additionally, volume plays a crucial role in confirming the pattern; ideally, volume should be higher on the left shoulder and decrease through the head, then pick up again during the formation of the right shoulder and the subsequent break below the neckline. This volume pattern adds credibility to the reversal signal, providing traders with a clearer indication of when to enter or exit trades based on the expected shift in market direction.
2. Double top
The Double Top pattern is a powerful chart formation that signals a potential reversal from an existing uptrend to a downtrend. It is characterized by two consecutive peaks at approximately the same level, with a moderate trough in-between, resembling the letter "M". This pattern is indicative of a scenario where the price attempts to surpass a certain level twice, but fails each time, suggesting that the momentum behind the asset's price increase is waning. The confirmation of the pattern occurs when the price falls below the support level formed at the trough between the two peaks, indicating that sellers have started to dominate the market and a downward trend is likely to ensue.
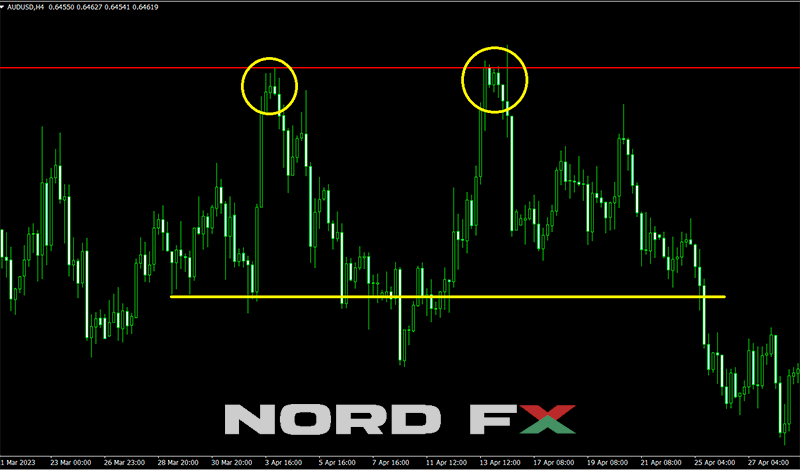
Traders and analysts closely monitor the development of a Double Top pattern as it provides a clear signal for potential entry or exit points. The level of the trough between the two peaks, often referred to as the neckline, becomes a critical area of focus. A break below this neckline is considered a confirmation of the pattern and a signal that the price is likely to continue falling. Volume analysis can further validate the pattern, with higher volume on the first peak and diminishing volume on the second peak being seen as a stronger indicator of an impending reversal. By recognizing and responding to Double Top formations, traders can make informed decisions to manage their positions and mitigate risk in a changing market environment.
3. Double bottom
The Double Bottom pattern is a bullish reversal configuration that signals a potential shift from a prevailing downtrend to an uptrend. It is easily identified by its "V" shape, formed by two consecutive troughs that are roughly equal in depth. This pattern emerges when the price of an asset tests a support level twice without breaking below it, indicating strong buying interest at this price level. The confirmation of the pattern occurs when the price moves above the resistance level established by the peak between the two troughs, suggesting that the momentum has shifted in favor of the buyers and that an upward trend may be starting.
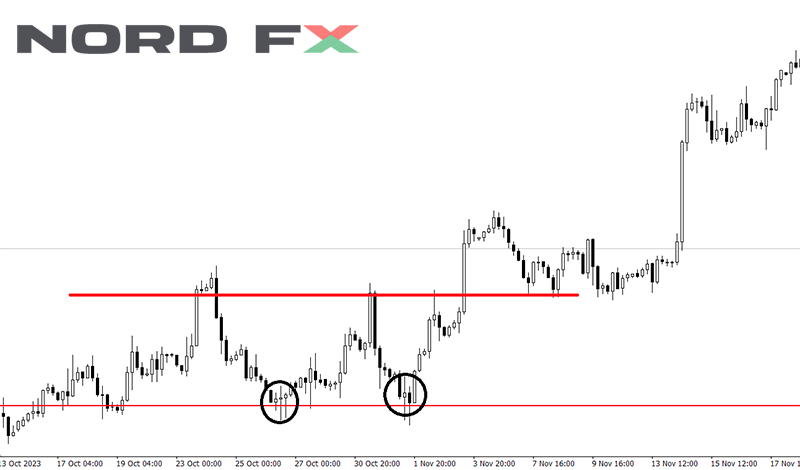
Traders often view the Double Bottom pattern as a significant indicator of changing market dynamics, offering a strategic point for entering long positions. The neckline, or the resistance level connecting the peak of the "V", becomes a focal point for this strategy. A decisive break above this level, particularly with increased trading volume, provides further confirmation of the pattern and the likelihood of a sustained upward movement. This pattern not only signals a potential entry point for traders but also helps in setting target prices and stop-loss orders, making it a valuable tool for planning trades and managing risk in anticipation of a market reversal.
4. Rounding bottom
The Rounding Bottom pattern, often referred to as a "saucer bottom," is a bullish reversal indicator that signifies a gradual and long-term shift from a downtrend to an uptrend. Characterized by a slow and steady decline followed by a gradual ascent forming a U-shaped curve on the chart, this pattern highlights a period of consolidation before the market sentiment shifts positively. Unlike sharp reversal patterns, the Rounding Bottom unfolds over an extended period, indicating a strengthening of buying pressure over time. The confirmation of the trend reversal is typically seen when the price breaks above the resistance level that marks the beginning of the formation. This pattern is particularly noteworthy for its implication of a sustained upward movement, offering traders the potential for significant gains as the new uptrend takes hold.
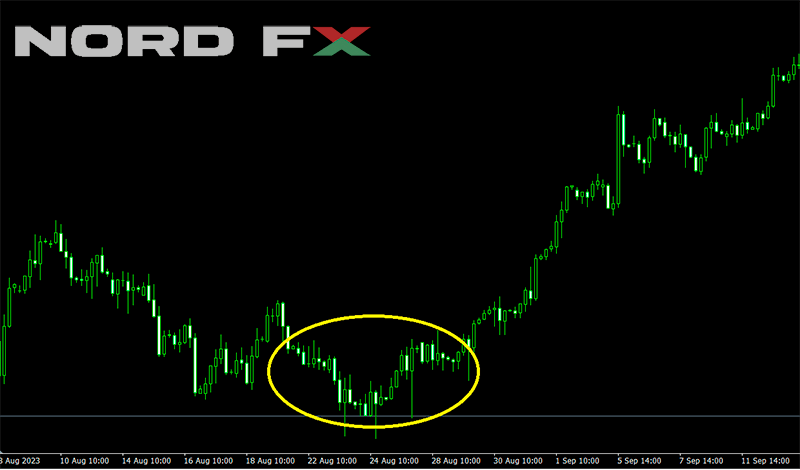
5. Cup and handle
The Cup and Handle pattern is a bullish chart formation that signals a reversal of an upward trend, characterized by its resemblance to a tea cup. This pattern begins with a downward drift in prices, forming the rounded bottom of the cup, followed by a rise back to the original starting point, and then a smaller retracement to form the handle. The "cup" part of the pattern typically exhibits a gentle, rounded bottom rather than a sharp V shape, indicating a consolidation phase where the market is stabilizing before a move up. The "handle" forms as a result of a slight downward correction, which is usually less deep and shorter in duration compared to the cup. The completion and confirmation of the Cup and Handle pattern occur when the price breaks out from the handle formation, surpassing the resistance level with increased volume.
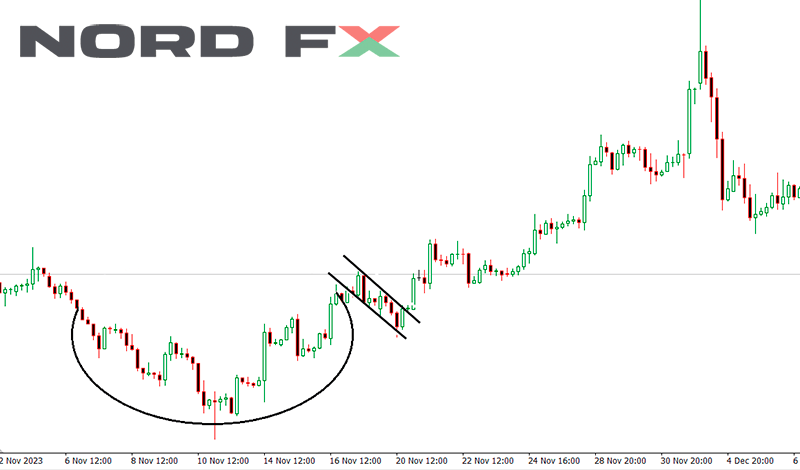
The duration of the pattern can vary, ranging from several weeks to months, making it applicable to both short-term traders and long-term investors. The key to trading this pattern successfully lies in identifying the proper breakout point, which is typically at the upper resistance level of the handle. A significant increase in volume on the breakout provides additional confirmation, suggesting that the upward trend is likely to persist. This pattern not only offers a clear entry point but also helps in setting realistic profit targets and managing risk, making it a favored strategy.
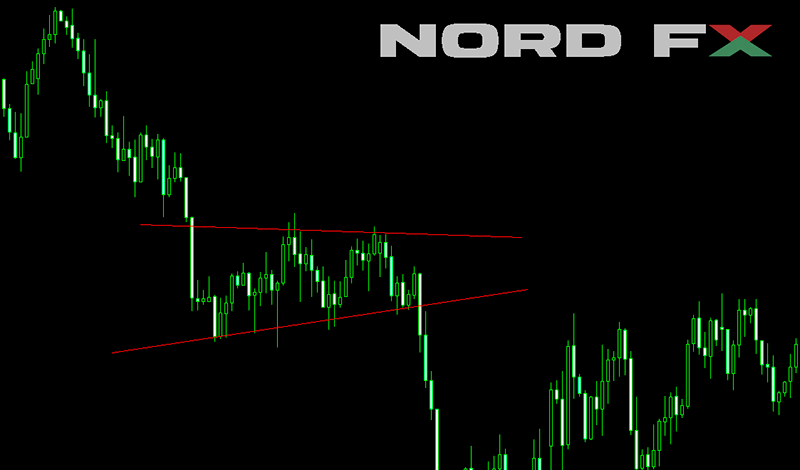
6. Wedges
Wedges are significant chart patterns characterized by converging trend lines over a period, indicating a pause or reversal in the current trend. They are classified into two types: rising wedges, which signal a potential bearish reversal during an uptrend, and falling wedges, which suggest a bullish reversal during a downtrend. These patterns are formed by a narrowing price range between support and resistance lines, reflecting a decrease in volatility and hinting at an imminent breakout. The validation of a wedge pattern comes with a clear break through one of the trend lines, accompanied by a noticeable increase in volume, guiding traders on potential entry or exit points. Whether signaling continuation or reversal, wedges are pivotal for traders in forecasting market movements and strategizing their trades accordingly.
7. Pennant or flags
Pennants and flags are short-term continuation patterns that signify a brief consolidation before the market resumes its prior trend. Both patterns are characterized by a sharp price movement followed by a sideways or slightly sloped consolidation, resembling a flag or pennant on a pole, hence their names. Flags are rectangular shaped, while pennants are small symmetrical triangles that form right after a significant price movement. The consolidation is typically accompanied by declining volume, and the completion of the pattern is confirmed when the price breaks out of the consolidation area in the direction of the initial sharp movement, often on increased volume. These patterns are highly valued by traders for their reliability in predicting the continuation of a trend, offering opportunities for strategic entry points in alignment with the market's prevailing momentum.
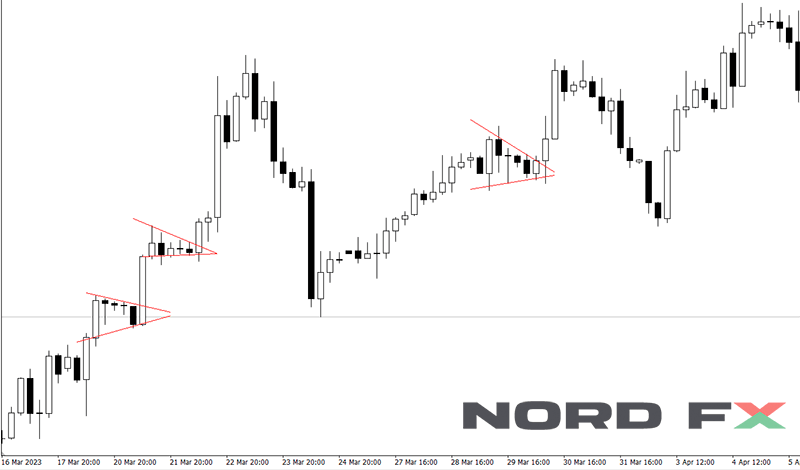
8. Ascending triangle
The Ascending Triangle is a bullish continuation pattern that forms during an uptrend, characterized by a flat upper resistance line and a rising lower support line that converge to form a triangle. This pattern indicates that buyers are more aggressive than sellers, as evidenced by the higher lows that push the price closer to resistance, suggesting a buildup of buying pressure. The completion and confirmation of the Ascending Triangle occur when the price breaks through the resistance level with significant volume, signaling a continuation of the prior uptrend. Traders often view this breakout as a strong buy signal, anticipating further upward momentum as the market confirms its bullish bias. The Ascending Triangle is particularly noteworthy for its clear entry and exit points, making it a favorite among traders looking to capitalize on sustained bullish trends.
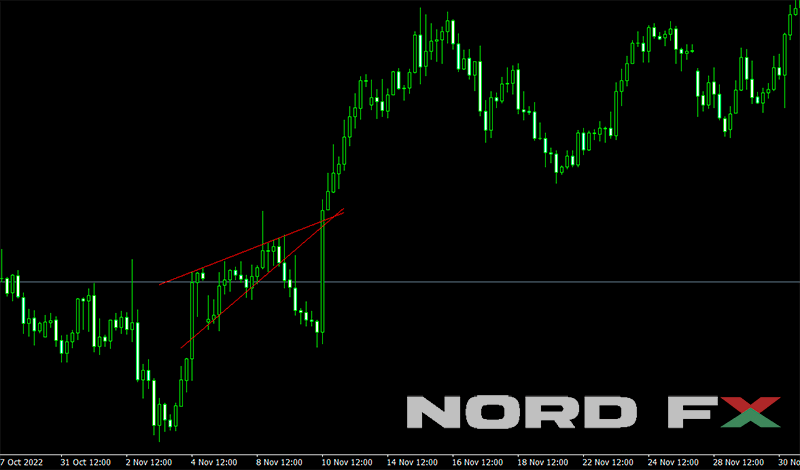
9. Descending triangle
The Descending Triangle is a bearish continuation pattern observed during a downtrend, marked by a descending upper trend line and a flat lower support line, converging to form a triangular shape. This pattern reflects the increasing pressure from sellers, as lower highs consistently test a level of support, indicating weakening demand at these price levels. The bearish signal is confirmed when the price breaks below the support line, often with an increase in volume, suggesting a continuation of the existing downtrend. Traders typically interpret this breakout as a sell signal, preparing for further declines in the price. The Descending Triangle is valued for its predictive reliability, offering traders strategic opportunities to position themselves in alignment with the market's downward momentum.
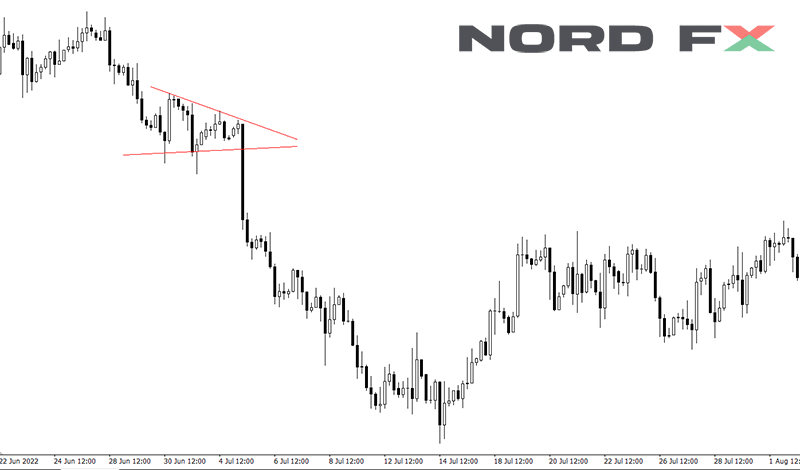
10. Symmetrical triangle
The Symmetrical Triangle pattern is a chart formation that signifies a period of consolidation before the price is forced to break out in a direction that confirms the market's next move. It is characterized by two converging trendlines of similar slope but in opposite directions, one connecting a series of progressively lower highs and the other connecting a series of higher lows, forming a symmetrical apex. This pattern reflects a balance between buyers and sellers, indicating that a breakout is imminent as the contraction of the price range continues and volatility decreases. The direction of the breakout, however, is uncertain until it occurs, making the Symmetrical Triangle a pattern of anticipation for traders.
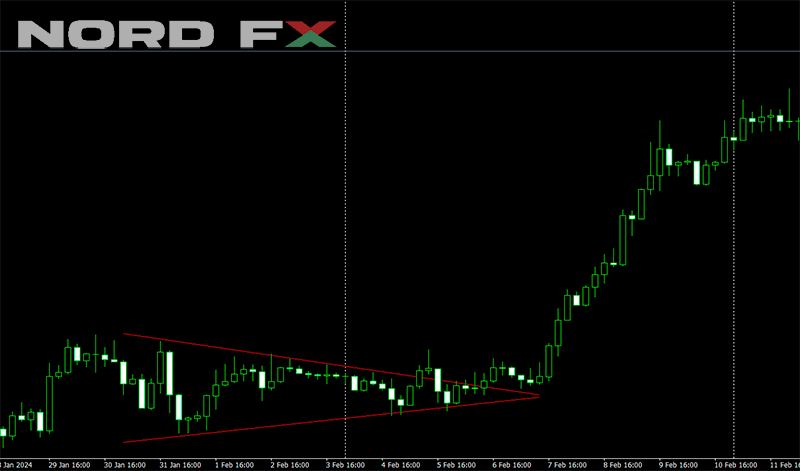
Upon the breakout, the Symmetrical Triangle can signal either a continuation of the prior trend or a reversal, depending on the direction of the price movement. Traders closely monitor the volume as a breakout with significantly increased volume is seen as a stronger signal of the pattern's validity and the sustainability of the ensuing trend. As such, the Symmetrical Triangle serves as a key indicator for potential entry and exit points, with traders often setting their positions in alignment with the breakout's direction. This pattern, with its non-directional bias, requires a careful approach, as the confirmation of the breakout direction is crucial for determining the subsequent market strategy.
Applying Chart Patterns to Intraday Trading
Identifying Patterns
Successful intraday trading involves identifying patterns early and accurately. Traders use various tools and indicators to enhance pattern recognition, including moving averages and volume analysis. As we have mentioned above, the increasing of volume strongly supports the anticipated price movement from the pattern.
Strategy Development
Once a pattern is identified, traders develop strategies around entry and exit points, stop-loss orders, and target prices. This strategic planning is crucial for managing risk and maximizing potential returns.
Analyzing Chart Patterns
Volume and Price Analysis
Volume plays a critical role in confirming chart patterns. An increase in volume alongside a pattern breakout is often seen as a confirmation of the pattern's validity.
Time Frames
Intraday traders analyze patterns across multiple time frames to gain a comprehensive view of the market. This multi-timeframe analysis helps in making more informed decisions.
The Role of Confirmation in Chart Patterns
Confirmation is a key aspect of trading chart patterns. It involves waiting for specific signals before executing a trade based on a pattern. For instance, a breakout on high volume is a common confirmation signal for both reversal and continuation patterns. This approach helps traders minimize false signals and improve the reliability of their trades.
Psychological Aspects
Chart patterns also reflect the psychological aspects of market participants. Patterns like head and shoulders or double tops reveal shifts in market sentiment, from bullish to bearish or vice versa. Understanding the psychology behind these patterns can provide traders with a deeper insight into market dynamics.
Risk Management
Effective risk management is integral to trading chart patterns. Traders often set stop-loss orders based on the pattern's parameters to protect against significant losses. For example, in a head and shoulders pattern, a stop-loss might be placed just above the pattern's neckline.
Tools and Resources for Chart Pattern Trading
Charting Software
Charting software is indispensable for intraday traders, offering advanced features for pattern analysis. Popular platforms include TradingView and MetaTrader.
Educational Resources
Understanding chart patterns requires continuous learning. Resources like the video - Ultimate Chart Patterns Trading Course on YouTube provide valuable insights into mastering chart patterns.
Advanced Charting Tools
Advanced charting tools offer features like automatic pattern recognition, which can help traders identify patterns more efficiently. These tools often come with a range of indicators and drawing tools that enable detailed analysis.
Trading Simulators
Trading simulators allow traders to practice identifying and trading chart patterns in a risk-free environment. This hands-on experience is invaluable for developing the skills necessary for successful intraday trading.
Online Forums and Communities
Online trading communities and forums can be excellent resources for learning and sharing knowledge about chart patterns. Engaging with a community of traders provides opportunities to gain insights from experienced traders and stay updated on the latest trends and strategies.
These resources can provide intraday traders with the necessary tools and knowledge to navigate the complexities of chart pattern trading effectively.
Intraday trading chart patterns are a powerful tool for traders, offering insights into market trends and potential price movements. By combining pattern analysis with other trading tools and resources, traders can develop robust strategies that cater to the fast-paced nature of the market. While this guide provides a comprehensive overview, continuous learning and practice are essential for mastering intraday trading chart patterns.
Remember, the key to successful intraday trading lies not just in understanding chart patterns but in integrating this knowledge with a disciplined trading strategy, effective risk management, and continuous learning.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Most Reliable Chart Patterns for Intraday Trading?
The reliability of chart patterns can vary based on market conditions, but some of the most trusted include:
- Head and Shoulders/Inverse Head and Shoulders: Known for signaling reversals.
- Triangles (Ascending, Descending, Symmetrical): Indicate continuation or reversal based on breakout direction.
- Flags and Pennants: Short-term continuation patterns that signal brief consolidations before a trend resumes.
How Long Does It Take to Learn Chart Pattern Trading?
The time it takes to learn chart pattern trading can vary widely among individuals. It depends on the time dedicated to studying, practicing, and trading. Generally, a few months of consistent learning and practice can provide a solid foundation, but mastery is an ongoing process.
Can Chart Patterns Be Applied to All Financial Markets?
Yes, chart patterns are applicable across various financial markets, including stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. The universal nature of these patterns stems from their foundation in market psychology, which is consistent across different asset classes.
How Important Is Volume in Confirming Chart Patterns?
Volume is crucial in confirming chart patterns. A significant change in volume during the formation of a pattern or at the breakout point provides additional confirmation of the pattern's validity and the potential for the anticipated price movement.
Are There Any Tools to Automatically Identify Chart Patterns?
Yes, many advanced charting platforms and trading software offer tools that can automatically identify chart patterns. These tools can help traders save time and improve accuracy in pattern recognition, though it's important for traders to manually verify these patterns to avoid false signals.
Advanced Strategies in Chart Pattern Trading
Combining Chart Patterns with Other Indicators
For enhanced accuracy, traders often combine chart patterns with other technical indicators such as moving averages, RSI (Relative Strength Index), and MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence). This multi-indicator approach helps in confirming the signals provided by chart patterns and in identifying the best entry and exit points.
The Importance of Backtesting
Backtesting involves testing a trading strategy using historical data to assess its viability. By backtesting strategies based on chart patterns, traders can refine their approach, adjust their risk management parameters, and improve their overall trading performance.
Psychological and Behavioral Aspects
Understanding the psychological and behavioral aspects behind chart patterns can give traders an edge. Market movements are often driven by human emotions such as fear and greed, which are reflected in chart patterns. Recognizing these psychological triggers can help traders anticipate market reactions more accurately.
How to identify and trade Intraday Chart Patterns?
Identifying and executing trades based on intraday chart patterns is a crucial aspect of day trading. Utilizing these patterns effectively can lead to well-informed trading decisions. Below are essential strategies for recognizing and trading with intraday chart patterns:
Technical Analysis Instruments
- Trend Lines: Utilize trend lines to determine market trends and possible trend reversals.
- Moving Averages: These tools help smooth out price data over a period, offering insights into the overall trend and areas of support and resistance.
- Volume Analysis: Examining the volume of trades in conjunction with price changes can indicate the robustness of a trend or signal potential reversals
Strategies for Entry and Exit
- Confirmation Signals: Look for additional indicators or pattern confirmations before committing to a trade to increase reliability.
- Setting Stop-Loss Orders: Implement stop-loss orders to minimize losses should the market move unfavorably.
- Determining Profit Targets: Define profit targets using technical analysis, such as support and resistance levels, to make informed exit decisions.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding Chart Patterns: Chart patterns are essential tools for intraday traders, providing insights into market sentiment and potential price movements.
- Types of Chart Patterns: There are several key patterns intraday traders should be familiar with, including head and shoulders, triangles, flags, and pennants.
- Application in Trading: Knowing how to identify and interpret these patterns can significantly enhance trading strategies by identifying entry and exit points.

